Vinyl Records Glossary
 If you’re a record collector, and you’re new to the hobby, you may encounter a number of terms in your searches for vinyl with which you’re unfamiliar.
If you’re a record collector, and you’re new to the hobby, you may encounter a number of terms in your searches for vinyl with which you’re unfamiliar.
To help, we’ve compiled this vinyl record collecting glossary of terms that you may find it helpful to know:
10” – Ten inch record. This size (25 cm) was used for both 78 RPM singles, made from the 1910s through the late 1950s, as well as long-play albums during the first years of album production (roughly 1948-1955.)
12” – Twelve inch record (30 cm). While this size is most commonly used for modern record albums (post-1955), this size record is also used occasionally for singles and extended-play (EP) recordings.
16 2/3 RPM – A playback speed for certain record albums, most commonly used for talking books for the blind. The slow playback speed allows for extra-long playing time, though the sound quality suffers as a result. Most of the people who own record players that are capable of playing 16 2/3 RPM records have never actually seen one, as they are not common.
180 gram – Weight of some modern era (post-1990) record pressings, usually those titles pressed as “audiophile” records. Most 12″ records pressed in earlier eras weighed between 125-150 grams. The heavier weight of these modern pressings is thought to provide better sound and less likelihood of warping.
200 gram – Weight of some modern (post-1990) record pressings, used by some manufacturers of “audiophile” records. 200 gram records are not seen as often as 180 gram pressings, and there is considerable debate in the audio community regarding the benefits of the additional 10% in weight, including the question of whether the added weight provides any benefits at all.
33 1/3 RPM – The speed used for nearly all long-play (LP) record albums from 1948 to the present day. This speed allows for longer playback time than the earlier 78 RPM pressing, and records at this speed usually offer up to 20 minutes of program material per side (though we’ve seen a few that played as long as 35 minutes, with reduced volume and sound quality.)
Click here to visit our rare records store.
45 RPM – The speed used since 1949 for most 7″ records, and occasionally for 12″ singles. Since the mid-1990s, a few record labels have reissued older recordings that were originally pressed at 33 1/3 RPM at the 45 RPM speed for improved sound quality, though this requires using more discs. A single disc album at 33 1/3 will usually take up two discs when pressed at 45 RPM.
78 RPM – Speed used from the 1910s through the late 1950s for 10″ singles. This format was rendered obsolete circa 1960 by the 45 RPM, 7″ single. Occasionally 78 RPM speeds have been used for certain promotional singles, usually as a marketing gimmick. Records pressed at this speed have had no commercial application for the past half century.
7” – Size of singles (usually one song per side) since 1949. These records normally play at 45 RPM, though a few have been released over the years that played at 33 1/3 RPM.

Acetate – Also known as a lacquer, an acetate is the first step in the record manufacturing process. An acetate is a lacquer-covered metal plate upon which the music is encoded via a lathe. You can read more about acetate records here.
Album – Originally a collection of 78 RPM, 10″ singles, collected in a binder. When the long-play album, containing a number of songs on a single disc, replaced 78 RPM albums in the early 1950s, the name remained.
Today, an “album” usually refers to a collection of songs recorded together and released as a single entity, usually one one disc, but sometimes released as multiple-disc sets.
Long-play albums were originally 10 inches in size, but modern albums are 12 inches in size.
Audiophile Record – Records pressed specifically to attract the attention of buyers who want (and are willing to pay for) albums with higher sound quality than regular mass-produced pressings.
Most audiophile records are pressed on more expensive vinyl that has less surface noise, and are mastered using tapes that are as close as possible to the original master tape. These pressings are usually on heavier (180-200 gram) vinyl and are sometimes cut at 45 RPM, rather than the standard 33 1/3.
Many audiophile records are intentionally released as limited edition pressings and sell for a premium price when new.
You can read more about audiophile records here.
Binaural Record – Short-lived early attempt to press records in stereo. These records required a special tonearm with two cartridges. Due to the awkwardness of the playback process and the expense of buying a special turntable or tonearm, these records were not commercially successful.
You can read more about binaural records here.
Bootleg Record – An album of previously unreleased material, pressed and released to the market without the knowledge or permission of the artist involved or their record company. Most bootleg records consist of previously unreleased studio recordings or live performances by popular artists.
You can read more about bootleg records here.
Bossa Nova – A form of music that originated in Brazil in the late 1950s, and popular through about 1967 or so. The music incorporated elements of samba and jazz and introduced the world to artists such as Sergio Mendes and Joao Gilberto. Many popular American artists (Frank Sinatra, Eydie Gorme, Stan Getz, and others) had success recording Bossa Nova.

Cheesecake – Term usually used to describe album covers that prominently feature attractive women, often in risque poses or dressed in minimal attire. Most often found on albums from the late 1950s and early 1960s.
Colored Vinyl – Term used to describe any record pressed from a color of vinyl other than black. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, some record companies routinely pressed records on colors other than black as a matter of course. Over time, colored vinyl records became limited to either promotional use or as limited edition releases.
You can read more about colored vinyl records here.
Counterfeit – A reproduction of a record, created by unscrupulous individuals with the intention of fooling the buyers into believing they are buying the genuine item. Most often found today with exceptionally rare titles, though in the 1970s, counterfeit copies of new releases were often mass produced and frequently found their way into major record stores.
You can read more about counterfeit records here.
Cover – The paper, cardboard, posterboard, or (rarely) plastic outer covering provided by the record company to hold a single or album. Covers usually have printed titles and often have a photo of the artist, as well as a listing of the contents of the record inside.
Cover Mouth – The portion of the cover that opens to allow for insertion and removal of the record. For albums, this is usually the right side of the cover as you look at the front. For 7″ singles, the opening is usually at the top.
CSG Process (also known as Haeco-CSG) – Short-lived process used from roughly 1968-1970 to compensate for vocals with too much volume when stereo records were played back on mono record players. CSG-encoded records were pressed during the time when monaural records were being phased out of the market.
This encoding solved the problem it was trying to fix while introducing others and was not popular with record buyers. Over time, record companies stopped using CSG encoding as the percentage of record buyers with stereo turntables increased to the point where it became unnecessary.

Cut Corner – A record album with a cover that has part of one of the corners cut off. This was done to indicate that the album had been discontinued (remaindered) and sold at a discount and that it was ineligible to be returned to the store for a refund. While many rare records are often found with cut corners, as many of them sold poorly when new, collectors usually prefer to buy copies that do not have a cut corner.
Cutout – Known in the book industry as a “remainder,” a cutout is a record that has been deleted from a record company’s catalog and is being sold at a discount to get rid of inventory the record company no longer wants.
Cutout albums are usually defaced in one of three ways – a drill or punch hole through the cover, removing a corner from the cover, or cutting a notch in the cover with a saw. These mark the records as being ineligible for a refund and while the covers are defaced, the records inside them are usually fully intact.
Dead Wax – The area immediately outside the label of a record that contains the runout groove and matrix numbers, but no recorded music. The dead wax area of a record is usually 1/4″-1″ wide.

Deep Groove – A ring found in the label area of some pressings from the mid-1950s through the early 1960s. This ring was an indentation, usually about 3″ in diameter, that was caused by certain types of pressing equipment. As record companies phased out that equipment by the mid-1960s, pressings with a deep groove may be indicative of original pressings, rather than later reissues.
Direct Metal Mastering (also known as DMM) – A process used in the manufacture of record albums where the music is cut to a solid metal plate, rather than a softer lacquer. There are advantages and disadvantages to this process, though many listeners prefer the sound of DMM pressings to the lacquer alternative. This process was often used in the late 1980s and early 1990s, and many records mastered using this process prominently have the letters “DMM” somewhere on the cover.
Direct to Disc – A process where the recorded material is performed live and recorded directly to acetate or lacquer, without first being recorded to magnetic tape. While the process produces better sound quality, direct to disc recording requires that an entire album side be recorded live in one take with no breaks. Direct to disc records are also, by necessity, limited edition pressings, as only a few lacquers can be cut at one time.
Double Album – An album containing two records, rather than the customary one.
Drill Hole – A hole drilled through the corner of an album (or less frequently, through the label) by a record company to indicate that the album has been discontinued and may not be returned for a refund. Most records with drill holes were sold at deeply discounted prices.

Duophonic – A proprietary system used by Capitol Records in the early 1960s to simulate stereo on material originally recorded in mono. Duophonic usually added a bit of a delay between the two channels and added reverberation to give a stereo effect to mono recordings.
Duophonic was created when record companies discovered that some buyers would only purchase stereo records, and it was an attempt to sell mono material to those buyers.
You can read more about Duophonic and other “fake stereo” pressings here.
Dynaflex – A short-lived manufacturing process used by RCA Records from 1969 to some time in the mid 1970s. To save money, RCA developed a process to press records using less vinyl than they’d been previously using. The result was a record that was exceptionally thin, more flexible than other records, and much more prone to warpage, though less prone to damage in shipping. On their record covers and inner sleeves, RCA promoted Dynaflex pressings as an improvement in the product. Buyers disagreed, and often disparagingly refer to Dynaflex as “Dynawarp.”
Dynagroove – Not to be confused with Dynaflex, Dynagroove developed by RCA Records in 1963 to improve the sound of their records on low-end playback equipment. This process increased bass in quiet passages while attempting to reduce high frequency distortion. Unfortunately, this only worked on phonographs with inexpensive conical needles and not more expensive elliptical ones. Owners of more expensive turntables thought the “new” process sounded much worse than the old one.
Audiophiles were unhappy with the process and the resulting sound, and RCA discontinued it about 1970 or so.

Exotica – A type of music introduced in the mid-1950s, usually attributed to pianist Martin Denny. Exotica attempted to introduce music from Asia, the Orient, and Africa to Western listeners, and the music from this short-lived fad often included tribal chants, gongs, and the sound of birds or insects to augment the music.
The popularity of music in the Exotica genre led to lots of backyard parties with people drinking Mai Tais while standing amidst Tiki torches. By the early 1960s, people had moved on from listening to Exotica when they discovered Bossa Nova.
Extended Play – Also known as an “EP”, this term is usually used to describe a 7″ single that plays more than one song per side. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, record albums were quite expensive, and priced at the equivalent of about $50 today.
Record companies occasionally took a 12 song album and sold it as three 7″ records that had four songs each, with pricing that allowed buyers to buy one disc alone or all of them.
Extended play singles were sometimes released as standalone releases of one disc with three or four songs. While the format was quite popular in Britain, it never really caught on in the United States.
In the modern (post-1965) era, an extended play record usually describes a 12 inch record with more than two songs but fewer songs than one might find on an album.
Foxing – The appearance of brown spots on picture sleeves or album covers as they age. Foxing can occur on all kinds of paper, but it’s most visible on white paper. For unknown reasons, foxing is quite common on album covers from Japan, and probably seven out of ten Japanese albums have some evidence of it.
Foxing is not an indication of wear or mistreatment by a previous owner. An album cover can be in mint, untouched condition and still exhibit foxing. It is simply an artifact of the aging process.
Garage Rock – Raw, unpolished rock and roll from the mid-1960s, inspired by relatively inexperienced musicians who often rehearsed and sometimes recorded in their home garage. Examples include the Castaways, the Sonics, and the Standells.
Gatefold Cover – A record cover that is intended to fold open like a book. Often the inside of a gatefold cover will include lyrics, liner notes, or additional photos of the artist.
Gold Record Award – A framed, gold-plated record, usually with an accompanying plaque, created to commemorate sales of $1 million (later 500,000 copies sold.) In the United States, “official” gold record awards have an RIAA logo, indicating that that organization has certified the sales of that particular record.
These awards are usually given by a record company to the artist, the producer, and other people who were instrumental in helping the album achieve that particular sales milestone.

Hype Sticker – A paper or plastic sticker attached to the shrink wrap or cover of an album, usually with the intention of drawing attention to one or more songs on the album in order to increase sales. Sometimes a hype sticker will indicate that the particular record is pressed on colored vinyl, contains a poster, or is in some way special.
In-House Record Award – A gold or platinum record award that does not have an RIAA certification on it; usually created by record companies to award to their own personnel, rather than to be giving to the artist.
In the collector’s market, in-house awards usually sell for lower prices than RIAA-certified awards.
Inner Sleeve – A paper or plastic sleeve included with a record album that is intended to protect the disc from coming in direct contact with the cover, as the rough surface of the cover might damage the record.
While many inner sleeves are plain paper or plastic, sometimes inner sleeves contain lyrics or other information about that specific recording. On other occasions, record companies used inner sleeves to advertise other albums that might be of interest to the listener or to provide technical information about stereo recordings (1950s) or quadraphonic recordings (1970s.)
Insert – Any piece of paper included with an album other than a poster or inner sleeve. The most common use of inserts is to provide the listener with lyrics to that particular album.
Instrumental – A recording of music that contains no vocals. This applies to most jazz, classical, and surf music recordings.

Jukebox EP – A 7 inch extended-play record manufactured exclusively for use in jukeboxes. Jukebox EPs were primarily made in the 1960s and 1970s, and were usually pressed in stereo and often included a hard cover, similar to an album cover.
A typical jukebox EP would include three songs on each side and come with a small paper reproduction of the album cover and a half a dozen paper “title strips” to be inserted in the jukebox so that customers could select them for play.
Label – The round piece of paper in the center of a record that lists the name of the artist, the name of the album or song, the name of the record company, and other information that may be useful to the buyer or listener.
Lacquer – Another (and more correct) term for an acetate.
Live Album – Usually, an album that contains a recording of an artist performing in an “in concert” setting before a live audience. Occasionally, a recording of a band performing in a studio collectively as a band, rather than recording vocals and instruments individually.
Live albums are often released as either contractual obligations or to provide fans with something to buy during an unusually long delay between releases of studio albums by a particular artist.
Many modern live albums are not entirely live and may contain multiple overdubs added to the live recording in the studio at a later date. A few live albums released over the years weren’t live recordings at all, but were simply studio recordings with overdubbed audience sounds.

Living Stereo – Name used by RCA Records from 1958-1963 for their stereo recordings, which often had a rich, and unusually lifelike recording quality. Many albums from the Living Stereo period in both classical and popular genres are highly valued by collectors.
LP – Technically, a trademarked term by Columbia Records (correctly printed as “Lp”) in the late 1940s to denote their then-new long-playing record format, which could theoretically play up to 26 minutes per side at 33 1/3 RPM.
Popularly, the term is most often used as a slang reference to a record album. (“Have you heard the new Metallica LP?”)
Marbled Vinyl – A record pressed from multicolored vinyl with the vinyl distributed in such a way that the record resembles marble.
Matrix Number – A stamped or handwritten number in the dead wax area of a record. Matrix numbers tell pressing plant employees which record they are making. Matrix numbers may also include an indicator as to which of a series of sequential stampers was used to make a particular record.
Monaural – A method of recording in which all of the music is contained in a single audio channel, and which may be heard through a single speaker. Until 1957, all records were monaural. From 1957-1968, most albums were sold in both mono and stereo.
You can read more about monaural records here.
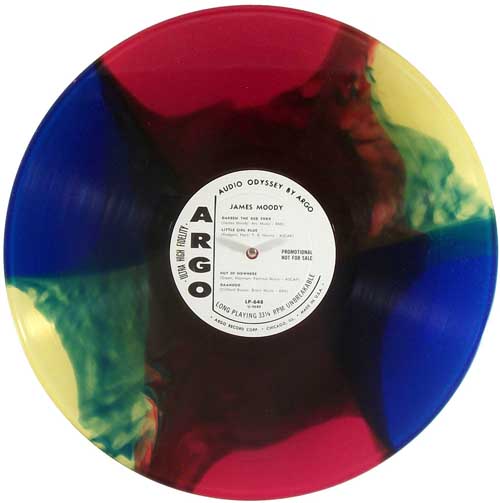

Multicolor Vinyl – A colored vinyl record that is comprised of two or more colors of vinyl on a single disc.
Obi – On Japanese albums (and some singles), a paper strip, usually about 2 inches wide, that wraps around the cover. The information printed on the obi is almost always in Japanese and includes information for the buyer that may not be printed on the cover.
Historically, many buyers discarded the obi shortly after purchase, as they are easily torn. In some cases, the presence (or absence) of an obi can dramatically affect the price of the record.
Original Cast Recording – A recording of the music, score, or songs from a play, performed by the cast of that play.
Picture Disc – A record pressed from two layers of clear vinyl with a paper image or photo sandwiched in between. Picture disc albums are usually limited edition or promotional items and are often packaged in covers with a die-cut window so that buyers can see the record itself.
The sound quality of picture discs is usually not as good as conventional pressings.
You can read more about picture discs here.
Picture Sleeve – A paper sleeve included with a record (usually a 7 inch single) that has a photo or image printed on it. Picture sleeves usually also list the artist and the name of the songs. Picture sleeves are usually limited in production and many are quite collectible.

Pirate Pressing – A record that contains material that has previously been released commercially but is pressed without authorization from the artist or the record company responsible for that material.
Often casually referred to as “bootlegs,” though that term actually refers to something else entirely.
You can read more about pirate pressings here.
Platinum Record Award – Similar to a gold record award, a platinum record award is a framed, silver-plated record, usually with an accompanying plaque, created to commemorate sales of 1 million copies of a particular album. In the United States, “official” platinum record awards have an RIAA logo, indicating that that organization has certified the sales of that particular record.
Play Hole – The hole in the center of a record that allows the record to fit over a turntable spindle. The hole and spindle keep the record properly centered on the platter so that it will play correctly.
Poster – A photographic insert included with an album that usually folds out to a size that is larger than the album cover itself. Occasionally included as a bonus with some titles, posters can often become quite rare with time, as many buyers hung them on the wall after purchase and failed to put them back in the album cover when they took them off of the wall at a later time.
Progressive Rock – A style of music popular from the late 1960s through the mid-1970s that featured long solos, fantasy lyrics and inventive song structures. Bands such as King Crimson, Yes, Emerson, Lake and Palmer, and Gong are examples of progressive rock bands.
Promo-only – A record release that was created to be distributed to radio stations or other promotional outlets, but was not intended for commercial sale. Promo-only releases often consisted of previously unavailable live material or compilations of recordings by a given artist intended to promote airplay.
Sometimes, promo-only titles contained the same material as commercial releases, but may have been in a different format from the commercial title, such as being pressed as a picture disc or on colored vinyl.
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, some albums that were commercially available only in stereo were released to radio stations in monaural as promo-only pressings.

Promotional Copy – A copy of a record that was pressed for distribution to radio stations or other promotional outlets, but were not pressed for retail sale. Most promotional copies of records have some print or indication on the label that they intended for promotional use, such as “Promotion Copy – Not for Sale” or some similar wording.
Promotional Stamp – A rubber stamped or machine stamped indicator on a record label or cover that indicates that the record is intended for promotional use only. Promotional stamps are usually used when record companies wish to use retail copies (“stock copies”) of records for promotional use.
Prototype – A record that was manufactured as an example of a potential release that was ultimately not released in that form. Prototype records are often pressed in very limited quantities and some are literally unique.
Examples of prototype records might be one-of-a-kind colored vinyl or picture disc pressings.
Provenance – The ability of a seller to demonstrate previous ownership or history of a particular record. Usually of interest to people buying unusual, one-of-a-kind items or items that are represented as being autographed by a particular artist.
Psych – Short for “psychedelic rock,” a short-lived style of rock music that was popular from roughly 1966 to 1970 that featured unusual chords, odd instrumentation, and frequently, long instrumental jams.
Psychedelic rock records were largely an underground phenomenon and many titles were privately pressed releases by artists that did not have national recognition. A number of psych records sell for hundreds or even thousands of dollars today.
Examples of psych artists include the 13th Floor Elevators, Mystic Siva, and the C.A. Quintet.

Punch Hole – A hole punched by machine through the corner of an album cover. Unlike drill holes, which were rough holes made with an electric drill a punch hole is a clean hole made by a machine. Punch holes are generally larger than drill holes and were most often used by record companies to indicate that the record was intended for promotional use.
Capitol Records frequently used punch holes to designate their promotional copies. Capitol sometimes used single punch holes and sometimes a series of very small holes that spelled out either the word “free” or the word “promo” in the corner of the cover.
Quadraphonic – A short-lived audio format during the early to mid-1970s that presented music in four channel sound, as opposed to the two channels of stereo.
Quadraphonic music was available in 8-track tape, LP, and reel to reel tape formats and required a four-channel amplifier (or two stereo amplifiers), four speakers, and a turntable, reel to reel tape deck or 8-track player capable of playing back quadraphonic records or tapes.
There were at least three different quadraphonic formats for records, and all were incompatible with the others. Format wars and equipment costs prevented the quadraphonic format from becoming popular.
Collectors are interested in quad records and tapes as the mixes are often dramatically different from the stereo versions of the same albums. In the case of a few quadraphonic records, the recordings are completely different from the stereo versions.
R&B – Short for “rhythm and blues” a term used by record companies in the 1950s to describe music that was primarily marketed to African-Americans. In record collecting, R&B can describe anything from Ray Charles to Robert Johnson to Motown.
Radio Show – A program of live concert performances, audio documentaries, or programs of music and interviews with recording artists intended for radio broadcast only. Syndicated shows such as the King Biscuit Flour Hour, Metalshop, Innerview, and Off the Record are examples of syndicated radio shows.
The live shows are often sought out by collectors of a given artist, and those recordings have often been the source material for bootleg records.

Rechanneled Stereo – Also known as “fake stereo,” rechanneled stereo was an audio format developed by various record companies in the early 1960s to accommodate buyers who refused to purchase any records that weren’t available in stereo. See also: Duophonic
Rechanneled stereo records often created a stereo effect from monaural recordings by using frequency separation, audio delay, and added reverb to make monaural recordings sound “kind of like” stereo, usually with poor results.
Records released in rechanneled stereo usually indicated it on the cover, saying things like “Electronically reprocessed to simulate stereo.” Rechanneled stereo records nearly always sell for lower prices than their mono counterparts.
You can read more about rechanneled stereo here.
Record Grading – A description of a record in terms of its physical condition in order to accurately describe it to potential buyers.
Most record grading is done using the Goldmine system of Mint, Very Good, Good and Poor, with a + or – used to denote grades in between. Some sellers, particularly those based in the UK, use the Record Collector system which uses Mint, Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair and Poor.
Record grading is highly subjective, due to the many ways a record can be worn or damaged.
Reissue – A later, rather than original, pressing of a record. Record companies used to delete titles that were no longer selling well, but they would occasionally return a title to print if they felt it was warranted by potential sales.
Such a later pressing is known as a “reissue,” and they’re almost always less desirable to collectors than original pressings.
ROIR – A Record Of Indeterminate Origin. Another term for a bootleg recording.
Saw Mark – A cut in an album cover, usually near a corner, literally made through the use of a saw. Used to mark a record as discontinued and to indicate that it may no longer be returned for a refund.
Sealed – A record that is still encased in shrinkwrap or a factory applied bag. Record companies begn sealing records in the early 1960s in order to prevent vandalism in stores and to assure buyers that the record inside was new and pristine.
Sealed copies of out of print titles often command a premium price among collectors.
Seam Split – A tear along an edge of an album cover, usually caused by the record inside or by improperly inserting or removing the record from the cover.

Shaped Record – A record in any shape other than round. Most often found in picture discs. Shaped records start as round records but are cut using a die shortly after being pressed. Shaped records may be triangular, square, rectangular, hexagonal, octagonal or cut to a custom shape.
Single – A record containing one or two songs, usually sold on the basis of one song alone. Most often found in a 7 inch size playing at 45 RPM, singles have also been sold in 10 inch (78 RPM) and 12 inch (33 1/3 or 45 RPM) sizes.
Soundsheet – Also known as a flexi-disc, a flexible record pressed from ultra-thin plastic. Soundsheets have historically been inserted in magazines or newspapers.
Soundtrack – A recording of a score, music, songs, or dialogue from a motion picture.
Spindle Mark – A physical mark or impression on a record label caused by an inaccurate attempt to place the record on a phonograph or turntable. An abundance of spindle marks, even on a record with little apparent wear, may indicate that the record has been played excessively and may exhibit unwanted noise during playback.

Splatter Vinyl – A record pressed from multicolored vinyl where the vinyl is spread across the record in a scattered, random pattern, rather than swirled, such as with marbled vinyl.
Spoken Word – A recording of someone speaking or reciting printed material, as opposed to singing.
Stamper – The metal plate used to press a record from a “biscuit” of vinyl.
Stamper Number – A number, written or stamped into the dead wax area of some records that indicates which of a sequential series of stampers was used to press that particular record.
Many collectors prefer earlier stamper numbers, either because that record was made closer to the album’s original release date or because records pressed from lower-numbered stampers often sound better than records pressed from higher-numbered stampers.
Not all record companies used user-recognizable systems for denoting stamper numbers, though there are exceptions:
Stamper numbers are easily identified on records by RCA, where the matrix number ends with a dash, a number, and the letter “S.” Example: “-1S”
Other record companies, such as Parlophone in the UK, used a coded system to identify stampers. You can read more about that system here.
Stereo – A recording format where the recorded material is presented in two distinct channels of sound, one on the left and one on the right. The de facto audio standard for records since 1968.
Stock Copy – A copy of a record that was pressed for commercial sale to the public, as opposed to a promotional copy, which was pressed for use by radio stations.
Surf Music – A style of rock music made popular during the early to mid-1960s. Surf music was originally instrumental, and featured distorted guitars with lots of added reverberation. Dick Dale and bands such as the Surfaris and the Chantays specialized in this type of music.
Instrumental surf was later augmented by adding vocals, with the Beach Boys and Jan and Dean being good examples.
Test Pressing – A copy of a record manufactured expressly for evaluation purposes by record company personnel or the artists or producers involved in the recording of that record. Test pressings are often indicated with custom labels that say “test pressing” or blank labels with no information at all.
Test pressings are often identical in sound to later stock copies of that same record, though sometimes test pressings appear on the market that contain earlier versions of songs or songs that were eventually discarded before the album was released.
Timing Strip – A strip of paper, usually 2 to 4 inches in width and about 12 inches wide, that appears on the covers of promotional copies of many albums from the 1960s and 1970s.
This strip usually listed all of the song titles on the album, publishing information, and the running times of the songs.
Sometimes a timing strip included a checkbox next to each song title that allowed a radio station’s program director or disk jockey to indicate which songs they preferred to use for airplay.
Title Sleeve – A paper sleeve for a 7 inch single that has the name of the artist and the title of the song(s) printed on it, but not a photograph.
Similar to a picture sleeve, but without the photo.
UHQR – Ultra High Quality Record, a proprietary type of record pressed by JVC in Japan in the early 1980s. The UHQR was distinguished by its then-heavy 200 gram weight and its unusual “flat” profile in that the record had uniform thickness across its entire surface, where most records were thicker in the middle than they were at the edges.
Only a handful of JVC-pressed UHQR titles were ever released, and as far as we know, such titles were only released by Mobile Fidelity Sound Labs, Reference Recordings, and Telarc. All are highly collectible. The trademarked term UHQR is now owned by Acoustic Sounds, which has recently released a number of titles in that format.
Vinyl – Within the record collecting community, “vinyl” has multiple meanings. It can refer to the physical material used to manufacture a record, but it can also refer to the record format generically, as in, “I’m not going to buy Abbey Road on compact disc; I prefer to buy it on vinyl.”
Wax – Slang for vinyl; usually used by older collectors. “Red wax” and “red vinyl”, for example, are synonymous.
White Label Promo – A promotional copy of a record distinguished by having a white label with promotional indications on it (“Promotion Copy – Not for Sale”) that is distinctly different from the stock copies of the same record, which were sold with colored labels.











